257. Binary Tree Paths
Given the root of a binary tree, return all root-to-leaf paths in any order.
A leaf is a node with no children.
Example 1:
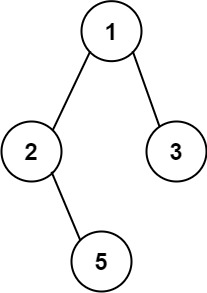
Input: root = [1,2,3,null,5] Output: ["1->2->5","1->3"]
Example 2:
Input: root = [1] Output: ["1"]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 100]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
recursion
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) {
vector<string> res;
dfs(root, "", res);
return res;
}
void dfs(TreeNode* root, string out, vector<string>& res) {
if(!root->left && !root->right) {
res.push_back(out + to_string(root->val));
}
if(root->left) {
dfs(root->left, out + to_string(root->val) + "->", res);
}
if(root->right) {
dfs(root->right, out + to_string(root->val) + "->", res);
}
}
};
- T:
- S:
iteration
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) {
vector<string> res;
// base case
if(!root) return res;
// 如果沒有左右子節點,則返回 root
if(!root->left && !root->right) {
return {to_string(root->val)};
}
// 找左側
for(auto s : binaryTreePaths(root->left)) {
res.push_back(to_string(root->val) + "->" + s);
}
// 找右側
for(auto s : binaryTreePaths(root->right)) {
res.push_back(to_string(root->val) + "->" + s);
}
return res;
}
};
- T:
- S: