234. Palindrome Linked List
Given the head of a singly linked list, return true_ if it is a _
palindrome
_ or false otherwise_.
Example 1:
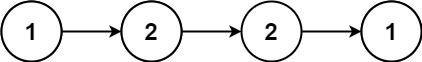
Input: head = [1,2,2,1] Output: true
Example 2:
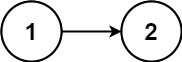
Input: head = [1,2] Output: false
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[1, 105]. 0 <= Node.val <= 9
判斷 linked list 是否有迴文
解法一:遞迴
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isPalindrome(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* cur = head;
return helper(head, cur);
}
bool helper(ListNode* head, ListNode*& cur) {
if (!head) return true;
bool res = helper(head->next, cur) && (cur->val == head->val);
cur = cur->next;
return res;
}
};
- T:
- S:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isPalindrome(ListNode* head) {
if (!head || !head->next) return true;
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* fast = head;
stack<int> stk;
stk.push(head->val);
while (fast->next && fast->next->next) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
stk.push(slow->val);
}
if (!fast->next) stk.pop();
while (slow && slow->next) {
slow = slow->next;
int tmp = stk.top(); stk.pop();
if (tmp != slow->val) return false;
}
return true;
}
};
- T:
- S:
不用 stack,空間複雜度 的解法
- T:
- S: