61. Rotate List
Given the head of a linked list, rotate the list to the right by k places.
Example 1:
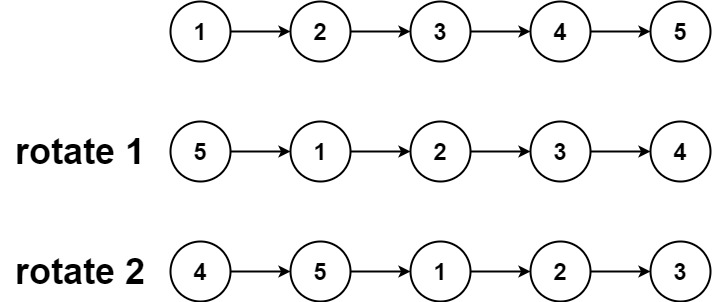
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2 Output: [4,5,1,2,3]
Example 2:
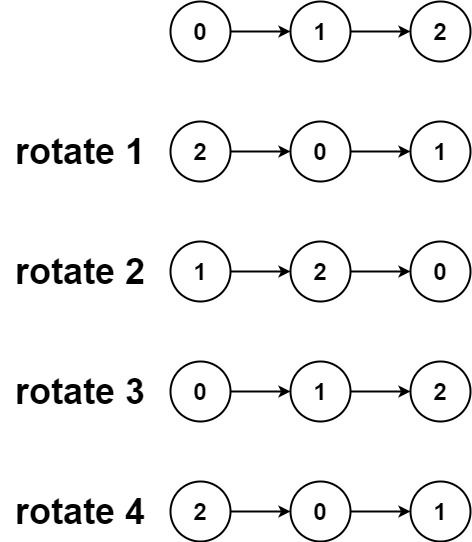
Input: head = [0,1,2], k = 4 Output: [2,0,1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[0, 500]. -100 <= Node.val <= 1000 <= k <= 2 * 109
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* rotateRight(ListNode* head, int k) {
// base case
if (!head || !head->next) return head;
// 計算 linked list 長度
ListNode* cur = head;
int n = 1;
while(cur->next) {
cur = cur->next;
++n;
}
// 接成一個環
cur->next = head;
// 因為也有 k 大於 n 的情況
// 所以這裡要做 k %= n 處理
k %= n;
// 再用一個 new_tail pointer 指向 head
// 新的節點的頭是從末端數回來第 k 個節點,所以是 n - k
ListNode* new_tail = head;
for (int i = 0; i < n - k - 1; ++i) {
// new_tail 移到新的節點的頭
new_tail = new_tail->next;
}
// 新的節點的 head = new_tail->next
// 以 head = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] 這個例子來說
// 現在的 new_head 指向 4
ListNode* new_head = new_tail->next;
// 斷開環
// 以 head = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] 這個例子來說
// 現在的 new_tail 指向 3,所以 new_tail->next 要指向 NULL
new_tail->next = nullptr;
// 最後 retrun 新的起始點 head
return new_head;
}
};
- T:
- S: