232. Implement Queue using Stacks
Implement a first in first out (FIFO) queue using only two stacks. The implemented queue should support all the functions of a normal queue (push, peek, pop, and empty).
Implement the MyQueue class:
void push(int x)Pushes element x to the back of the queue.int pop()Removes the element from the front of the queue and returns it.int peek()Returns the element at the front of the queue.boolean empty()Returnstrueif the queue is empty,falseotherwise.
Notes:
- You must use only standard operations of a stack, which means only
push to top,peek/pop from top,size, andis emptyoperations are valid. - Depending on your language, the stack may not be supported natively. You may simulate a stack using a list or deque (double-ended queue) as long as you use only a stack's standard operations.
Example 1:
Input ["MyQueue", "push", "push", "peek", "pop", "empty"] [[], [1], [2], [], [], []] Output [null, null, null, 1, 1, false]
Explanation MyQueue myQueue = new MyQueue(); myQueue.push(1); // queue is: [1] myQueue.push(2); // queue is: [1, 2] (leftmost is front of the queue) myQueue.peek(); // return 1 myQueue.pop(); // return 1, queue is [2] myQueue.empty(); // return false
Constraints:
1 <= x <= 9- At most
100calls will be made topush,pop,peek, andempty. - All the calls to
popandpeekare valid.
解法:使用兩個 stacks
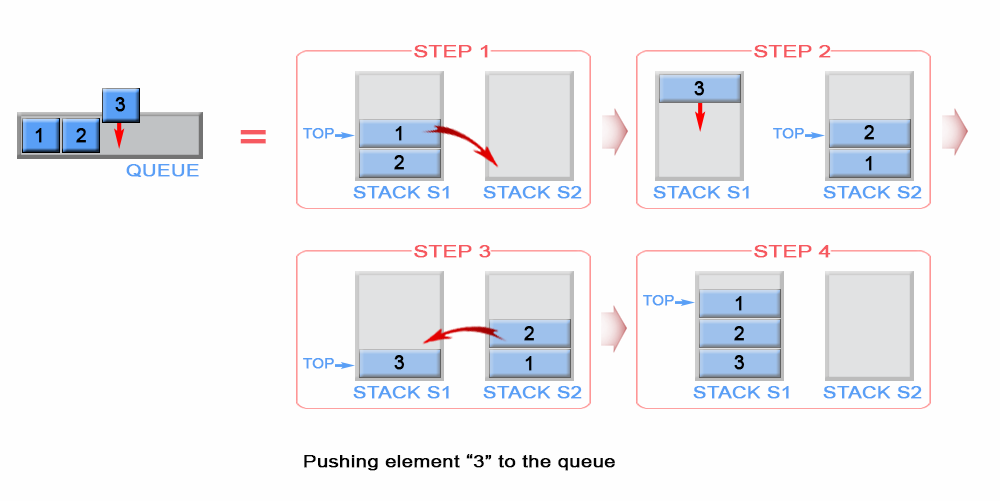
class MyQueue {
public:
MyQueue() {}
void push(int x) {
// 後進來的會維持在最上層
// 如果 s1 推了 1, 2, 3,3 會在最上面
s1.push(x);
}
int pop() {
peek();
int temp = s2.top(); s2.pop();
return temp;
}
int peek() {
// s2 用來儲存 s1 的反轉順序,如果 s2 裡面有值,直接回傳 s2.top();
if(!s2.empty()) return s2.top();
// 如果 s1 還有值,將元素丟到 s2 儲存,反轉順序
while(!s1.empty()) {
s2.push(s1.top()); s1.pop();
}
return s2.top();
}
bool empty() {
return s1.empty() && s2.empty();
}
private:
stack<int> s1; // push 進去的元素先裝在這,最後一個元素會維持在最上層
stack<int> s2; // 將 s1 的元素 pop() 到 s2,反轉順序
};
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue* obj = new MyQueue();
* obj->push(x);
* int param_2 = obj->pop();
* int param_3 = obj->peek();
* bool param_4 = obj->empty();
*/
- T:
- S: