417. Pacific Atlantic Water Flow
There is an m x n rectangular island that borders both the Pacific Ocean and Atlantic Ocean. The Pacific Ocean touches the island's left and top edges, and the Atlantic Ocean touches the island's right and bottom edges.
The island is partitioned into a grid of square cells. You are given an m x n integer matrix heights where heights[r][c] represents the height above sea level of the cell at coordinate (r, c).
The island receives a lot of rain, and the rain water can flow to neighboring cells directly north, south, east, and west if the neighboring cell's height is less than or equal to the current cell's height. Water can flow from any cell adjacent to an ocean into the ocean.
Return a 2D list of grid coordinates result where result[i] = [ri, ci] denotes that rain water can flow from cell (ri, ci) to both the Pacific and Atlantic oceans.
Example 1:
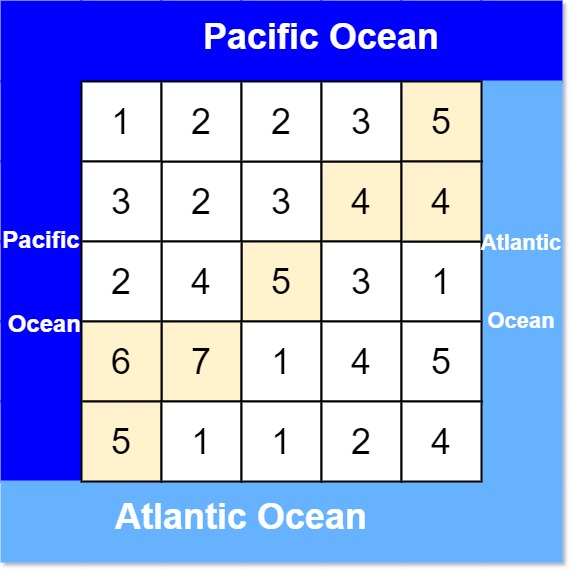
Input: heights = [[1,2,2,3,5],[3,2,3,4,4],[2,4,5,3,1],[6,7,1,4,5],[5,1,1,2,4]] Output: [[0,4],[1,3],[1,4],[2,2],[3,0],[3,1],[4,0]] Explanation: The following cells can flow to the Pacific and Atlantic oceans, as shown below: [0,4]: [0,4] -> Pacific Ocean [0,4] -> Atlantic Ocean [1,3]: [1,3] -> [0,3] -> Pacific Ocean [1,3] -> [1,4] -> Atlantic Ocean [1,4]: [1,4] -> [1,3] -> [0,3] -> Pacific Ocean [1,4] -> Atlantic Ocean [2,2]: [2,2] -> [1,2] -> [0,2] -> Pacific Ocean [2,2] -> [2,3] -> [2,4] -> Atlantic Ocean [3,0]: [3,0] -> Pacific Ocean [3,0] -> [4,0] -> Atlantic Ocean [3,1]: [3,1] -> [3,0] -> Pacific Ocean [3,1] -> [4,1] -> Atlantic Ocean [4,0]: [4,0] -> Pacific Ocean [4,0] -> Atlantic Ocean Note that there are other possible paths for these cells to flow to the Pacific and Atlantic oceans.
Example 2:
Input: heights = [[1]] Output: [[0,0]] Explanation: The water can flow from the only cell to the Pacific and Atlantic oceans.
Constraints:
m == heights.lengthn == heights[r].length1 <= m, n <= 2000 <= heights[r][c] <= 105
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> directions = {{0, -1}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};
vector<vector<int>> pacificAtlantic(vector<vector<int>>& heights) {
int rows = heights.size(), cols = heights[0].size();
if(rows == 0 || cols == 0) return {};
vector<vector<int>> res;
// 分別用兩個矩陣紀錄這個格子有沒有比其他格子高
// 起始值都是 false
vector<vector<bool>> pacific(rows, vector<bool>(cols));
vector<vector<bool>> atlantic(rows, vector<bool>(cols));
// by rows 開始搜索,如果發現這個格子比周圍的格子高,就標記 true
// 因為要找比周圍格子高的值,起始值用 INT_MIN
for(int i = 0; i < rows; ++i) {
dfs(heights, pacific, INT_MIN, i, 0);
dfs(heights, atlantic, INT_MIN, i, cols - 1);
}
// by cols 開始搜索,如果發現這個格子比周圍的格子高,就標記 true
// 因為要找比周圍格子高的值,起始值用 INT_MIN
for(int j = 0; j < cols; ++j) {
dfs(heights, pacific, INT_MIN, 0, j);
dfs(heights, atlantic, INT_MIN, rows - 1, j);
}
for(int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
if(pacific[i][j] && atlantic[i][j]) {
res.push_back({i, j});
}
}
}
return res;
}
void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& heights, vector<vector<bool>>& seen, int previous, int i, int j) {
int rows = heights.size(), cols = heights[0].size();
if(i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= rows || j >= cols || seen[i][j] || heights[i][j] < previous)
return;
// 標記這個格子比其他人高
seen[i][j] = true;
// 四個方向深度搜索
for(auto& dir : directions)
dfs(heights, seen, heights[i][j], i + dir[0], j + dir[1]);
}
};
- T:
- S: